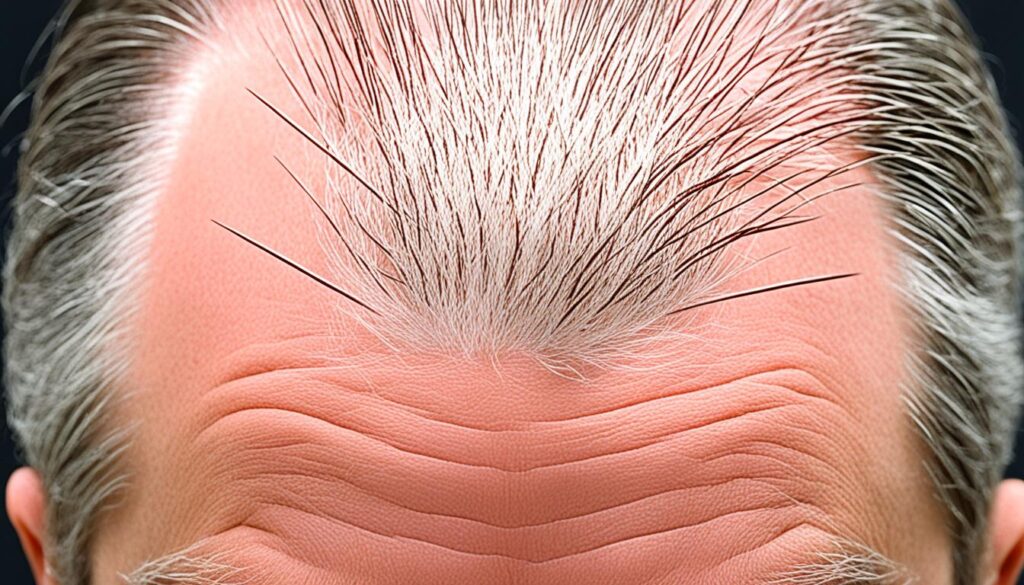
Experiencing hair loss can be a distressing experience, especially for women. Frontal balding in females, also known as female pattern baldness, is a common condition that affects many women worldwide. It is characterized by the thinning of hair, particularly in the frontal area of the scalp, leading to a receding hairline.
There are several factors that can contribute to frontal balding in females. Genetic factors play a significant role, as female pattern baldness tends to run in families. Hormonal changes, such as fluctuations in androgens, including dihydrotestosterone (DHT), also contribute to the development of female pattern baldness.
Treatment options for frontal balding in females aim to prevent further hair loss and promote hair regrowth. These include topical medications like minoxidil and oral medications such as spironolactone, which can help stimulate hair growth. In more advanced cases, hair transplant surgery may be an option to restore hair in the affected areas.
Prevention is also an essential aspect of managing frontal balding in females. Taking care of the hair and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help maintain hair health and minimize hair damage. Avoiding tight hairstyles, protecting the hair from sun damage, and eating a balanced diet rich in protein and essential vitamins are key preventive measures.
If you are experiencing excessive hair loss or noticeable thinning, it is important to consult with a doctor or dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They can evaluate your individual case and recommend the best course of action to address your frontal balding concerns.
Key Takeaways:
- Frontal balding in females, also known as female pattern baldness, is characterized by excessive hair loss and thinning in the frontal area of the scalp.
- Genetic factors and hormonal changes, such as fluctuations in androgens, contribute to the development of frontal balding in females.
- Treatment options for frontal balding in females include topical medications like minoxidil, oral medications such as spironolactone, hair transplant surgery, and preventive measures.
- Preventive measures include avoiding tight hairstyles, protecting the hair from sun damage, and maintaining a healthy diet.
- Consulting with a doctor or dermatologist is essential for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Understanding Female Pattern Baldness
Female pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is a hereditary condition that results in hair loss and thinning in women. Unlike in men, female pattern baldness does not typically lead to complete baldness, but rather a gradual reduction in hair density. This condition is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic factors and hormonal changes, such as fluctuations in androgens, including dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Women experiencing female pattern baldness may notice a widening part, general hair thinning, or a receding hairline that differs from the pattern seen in men.
“Female pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common form of hair loss in women. It is estimated to affect about 40% of women by the age of 50.”
To understand the causes and treatment options for female pattern baldness, it is important to first understand the underlying factors contributing to this condition. Genetic factors play a significant role, as female pattern baldness tends to run in families. Hormonal changes, such as the fluctuation of androgens, also contribute to hair loss and thinning in women.
The Role of Genetic Factors
Genetic factors are known to play a key role in female pattern baldness. If a woman has a family history of this condition, she is more likely to experience hair loss herself. Certain genes passed down from parents can influence how sensitive hair follicles are to the presence of androgens, leading to hair loss and thinning over time.
Hormonal Changes and Androgens
Fluctuations in hormones, particularly androgens like DHT, can contribute to the development of female pattern baldness. Androgens can bind to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner, shorter hair. Over time, this can result in a noticeable reduction in hair density. Hormonal changes can occur during various stages in a woman’s life, such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, which may trigger or worsen hair loss in genetically susceptible individuals.
The Different Presentation in Women
Female pattern baldness typically presents differently in women compared to men. While men often experience a receding hairline or bald spot at the crown of the head, women tend to experience a more diffuse pattern of hair loss. This can make it more challenging to diagnose female pattern baldness in its early stages, as the symptoms may be less noticeable or mistaken for other factors, such as styling practices or temporary shedding due to hormonal changes.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you suspect you may be experiencing female pattern baldness or significant hair thinning, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, who specializes in hair loss and scalp conditions. They can perform a thorough evaluation, take into account your medical history, and provide a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
| Common Symptoms of Female Pattern Baldness | Distinct Features in Women |
|---|---|
|
|
Causes of Frontal Balding in Females
Frontal balding in females can be caused by various factors. Understanding these causes is essential for determining the appropriate treatment approach. The following are some of the main causes of female pattern baldness:
- Genetic Factors: Female pattern baldness tends to run in families, indicating a strong genetic component. Certain genes can make a woman more susceptible to hair loss in the frontal area of the scalp.
- Health Conditions: Certain health conditions can contribute to frontal balding in females. Autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata, where the immune system attacks the hair follicles, can lead to hair loss. Additionally, hormonal imbalances and medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also contribute to hair thinning and loss in women.
- Medication Use: Some medications, such as cancer treatments like chemotherapy drugs, can cause temporary hair loss. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the potential side effects of medications and their impact on hair health.
- Tight Hairstyles: Wearing tight hairstyles that pull on the hair, such as braids, ponytails, or buns, can lead to traction alopecia. This condition occurs when constant pulling on the hair causes damage to the hair follicles, resulting in hair loss and thinning in the front of the scalp.
Identifying the underlying cause of frontal balding in females is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. By addressing the root cause, appropriate steps can be taken to prevent further hair loss and promote hair regrowth.
Comparison of Causes of Frontal Balding
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Female pattern baldness tends to run in families |
| Health Conditions | Autoimmune diseases, hormonal imbalances, and medical conditions |
| Medication Use | Side effects of certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs |
| Tight Hairstyles | Wearing hairstyles that pull on the hair, causing traction alopecia |
In the next section, we will explore the various treatment options available for frontal balding in females, including both non-surgical and surgical approaches.
Treatment Options for Frontal Balding in Females
Treatment options for frontal balding in females aim to prevent further hair loss and promote hair regrowth. There are several effective treatments available that can help women combat hair loss and regain their confidence. These treatments include:
- Minoxidil: This is a topical medication that is applied directly to the scalp. It works by promoting blood flow to the hair follicles and stimulating hair growth. Minoxidil is available over-the-counter and is one of the most commonly used treatments for women’s hair loss. It can prevent further hair thinning and even promote regrowth in some cases.
- Spironolactone: This is an oral medication that is typically used to treat high blood pressure. However, it can also be effective in treating hair loss in women. Spironolactone works by blocking the production of androgens, which can contribute to hair loss. It is commonly prescribed for women with female pattern baldness.
- Hair Transplant: In more advanced cases of frontal balding, hair transplant surgery may be an option. This procedure involves taking hair from a donor area, usually the back of the scalp or other parts of the body, and transplanting it to the balding area. Hair transplant surgery can provide long-lasting results and restore a fuller head of hair.
- Laser Treatment: Another emerging treatment option for women’s hair loss is laser therapy. Low-level laser light therapy is believed to stimulate hair growth by increasing energy production in the hair follicles. It is a non-invasive and painless treatment that can be done in a clinic or at home using a laser device.
It is important to note that not all treatments may be suitable for every individual. Consulting with a dermatologist or hair loss specialist can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the severity of the hair loss and individual needs.
Advancements in Hair Loss Treatment
“The field of hair loss treatment is continuously evolving, and researchers are constantly exploring new approaches to combat hair loss in women. With advancements in technology and medical research, we can expect to see even more effective and innovative treatments in the future.”
Preventing Frontal Balding in Females
While female pattern baldness may not always be preventable, there are steps that can be taken to keep the hair as healthy as possible and minimize hair damage. By following these hair care tips and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can promote hair health and reduce the risk of frontal balding.
Limit Damaging Hair Treatments
It’s important to be mindful of the treatments and styling techniques you use on your hair. Perming, straightening, and other harsh chemical treatments can weaken the hair and lead to breakage and hair loss. Limit the use of these treatments, opting for more natural hairstyles that minimize tension on the hair follicles.
Embrace a Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy hair. Ensure you’re getting enough nutrients, including protein, vitamins (especially vitamin A, vitamin E, and biotin), and minerals like iron and zinc. These essential nutrients support hair growth and strength, preventing hair loss and promoting overall hair health.
Protect Your Hair from the Sun
Excessive sun exposure can damage the hair and scalp, leading to dryness, brittleness, and increased hair loss. When spending time outdoors, protect your hair by wearing a hat or using a scarf to shield it from harmful UV rays. This simple step can help maintain the health and vitality of your hair.
“Limiting damaging hair treatments, embracing a healthy diet, and protecting your hair from the sun are key steps in preventing frontal balding in females.”
Avoid Brushing Wet Hair
Wet hair is more fragile and prone to breakage. Instead of using a brush, opt for a wide-tooth comb or simply use your fingers to detangle wet hair. This gentle approach will minimize hair breakage and preserve the integrity of your locks.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your hair care routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of frontal balding in females. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist if you notice excessive hair loss or have concerns about the health of your hair.
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia: A Specific Type of Hair Loss
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a specific type of hair loss that primarily affects the frontal area of the scalp. It is characterized by the destruction of hair follicles, which leads to permanent hair loss.
The exact cause of frontal fibrosing alopecia is unknown, but it is believed to be related to autoimmune factors. This condition typically starts with a receding hairline that gradually progresses and can also cause hair loss in other areas of the body.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent further permanent hair loss.
Understanding Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a specific type of hair loss that primarily affects the frontal area of the scalp. It is not contagious and is believed to be caused by a combination of immune system dysfunction and genetic factors.
This condition typically starts with a receding hairline and can progress to involve other areas of the scalp. Frontal fibrosing alopecia is more commonly diagnosed in women, particularly after menopause, although it can occur earlier in life.
The age of onset can vary, but most women notice hair loss about two to 12 years after starting menopause. The progression of frontal fibrosing alopecia can be slow, leading to permanent hair loss over time.
Causes of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia:
The exact cause of frontal fibrosing alopecia is unknown, but it is believed to be related to autoimmune factors. It is thought that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles in the affected areas, leading to their destruction and subsequent hair loss. Genetic factors also play a role in predisposing individuals to this condition.
Symptoms of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia:
- Receding hairline
- Thinning of hair in the frontal area of the scalp
- Redness or inflammation of the scalp
- Loss of eyebrow hair
- Loss of eyelashes
- Loss of body hair
Progression of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia:
The progression of frontal fibrosing alopecia can vary from person to person. In some cases, the hair loss may stabilize after a certain point, while in others, it may continue to progress. It is important to note that frontal fibrosing alopecia can lead to permanent hair loss, as the affected hair follicles are destroyed and cannot regenerate.
Please refer to the table below for a summary of the understanding of frontal fibrosing alopecia:
| Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia | |
|---|---|
| Contagious | No |
| Causes | Immune system dysfunction and genetic factors |
| Symptoms | Receding hairline, thinning hair, scalp redness, loss of eyebrow and eyelash hair, loss of body hair |
| Age of Onset | Varies, but typically occurs 2-12 years after menopause |
| Progression | Can be slow, leading to permanent hair loss |
Conclusion
Frontal balding in females, also known as female pattern baldness, can have a significant impact on a woman’s self-confidence and self-image. It is a condition characterized by excessive hair loss and thinning, particularly in the frontal area of the scalp. However, there are various treatment options available to help prevent further hair loss and promote hair regrowth.
Topical medications like minoxidil and oral medications such as spironolactone are commonly used to address female pattern baldness. These treatments can stimulate hair growth and prevent further hair thinning. In more advanced cases, hair transplant surgery and laser treatment can be considered as effective options for hair restoration.
Preventive measures are also crucial in maintaining hair health and minimizing hair damage. Taking care of the hair by avoiding harsh styling techniques, such as perming and straightening, and adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and sun protection can make a significant difference. Regular consultations with a doctor or dermatologist are recommended for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Frontal balding in females may be a challenging experience, but with the right treatment options, prevention strategies, and support, women can regain their confidence and achieve a healthier, fuller head of hair.
FAQ
What is female pattern baldness?
Female pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a type of hair loss that primarily affects women. It is characterized by excessive hair loss and thinning, particularly in the frontal area of the scalp.
What causes female pattern baldness?
The exact cause of female pattern baldness is not fully understood, but it is believed to be influenced by genetic factors, hormonal changes, and certain health conditions.
What are the treatment options for frontal balding in females?
Treatment options for frontal balding in females include minoxidil, oral medications like spironolactone, hair transplant surgery, and laser treatment.
How can I prevent frontal balding in females?
While female pattern baldness may not always be preventable, there are steps that can be taken to keep the hair as healthy as possible and minimize hair damage, such as limiting treatments that can damage the hair and eating a balanced diet rich in protein and essential vitamins.
What is frontal fibrosing alopecia?
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a specific type of hair loss that primarily affects the frontal area of the scalp. It is characterized by the destruction of hair follicles, which leads to permanent hair loss.
What causes frontal fibrosing alopecia?
The exact cause of frontal fibrosing alopecia is unknown, but it is believed to be related to autoimmune factors.
Is frontal fibrosing alopecia contagious?
No, frontal fibrosing alopecia is not contagious.
At what age does frontal fibrosing alopecia typically occur?
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is more commonly diagnosed in women, particularly after menopause, although it can occur earlier in life.
What is the best treatment for frontal balding in females?
The best treatment for frontal balding in females depends on the individual and the severity of the condition. Treatment options may include minoxidil, spironolactone, hair transplant surgery, or laser treatment.
How can I maintain hair health and minimize hair damage?
Taking care of the hair by avoiding treatments that can damage it, eating a healthy diet, and protecting it from sun damage can help maintain hair health and minimize hair damage.
When should I see a doctor for excessive hair loss?
If you are experiencing excessive hair loss, it is important to consult with a doctor or dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.