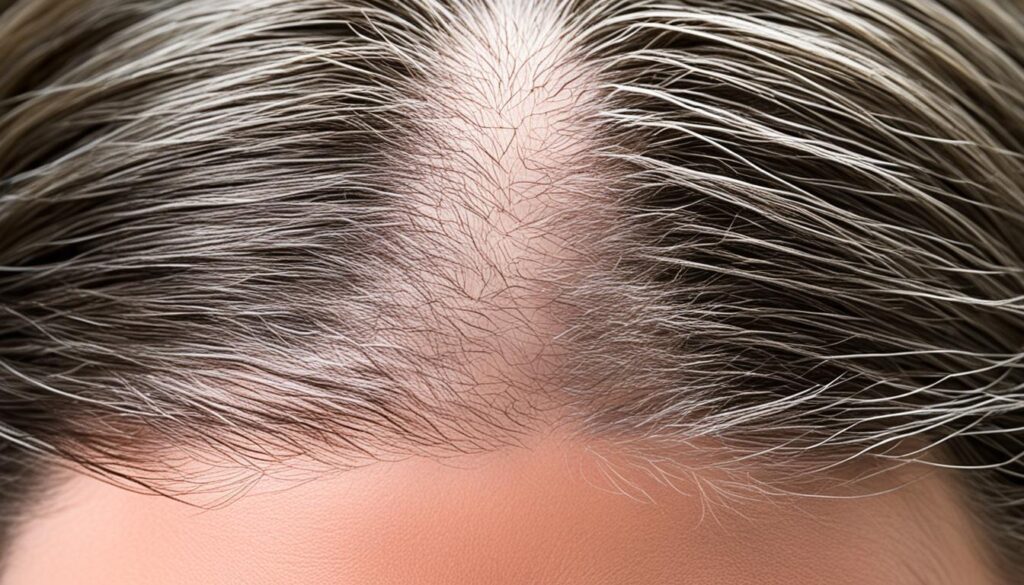
Genetic alopecia, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common form of hair loss that affects both men and women. In females, it is characterized by hair thinning at the top of the head and widening of the middle part, creating a pattern known as female pattern hair loss.
This condition is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Androgens, such as dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a significant role in causing hair loss. Variations in the AR gene, which codes for androgen receptors, have been linked to androgenetic alopecia. Additionally, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also contribute to hair loss in women.
About 30 million women in the United States are affected by genetic alopecia, which can start in the teenage years and is more likely to occur after menopause. It is essential to understand the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options available for this condition to effectively manage it.
Key Takeaways:
- Genetic alopecia, or female pattern hair loss, is a common condition in women.
- It is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, with androgens playing a significant role.
- Variations in the AR gene have been associated with androgenetic alopecia.
- About 30 million women in the United States are affected by genetic alopecia.
- Understanding the causes and available treatment options is crucial for managing this condition.
Causes of Androgenetic Alopecia in Females
Understanding the causes of androgenetic alopecia in females is key to managing and treating this condition. While the exact causes are not fully understood, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and hormonal factors.
One significant factor is aging, as hair follicles become more sensitive to androgens over time. Changes in hormone levels, particularly androgens like dihydrotestosterone (DHT), can also contribute to hair loss. Additionally, a family history of male or female pattern baldness increases the risk of developing androgenetic alopecia.
Other factors that may play a role in the development of androgenetic alopecia in females include heavy menstrual bleeding and certain medications, such as estrogenic oral contraceptives. These medications can influence hormone levels and potentially contribute to hair thinning and loss.
| Causes of Androgenetic Alopecia in Females | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Hormonal Changes | Family History | Heavy Menstrual Bleeding | Medications |
Research has also shown that variations in the AR gene, which codes for androgen receptors, are associated with androgenetic alopecia in both men and women. These genetic variations result in androgen receptors that are more easily stimulated by androgens, leading to increased activity in hair follicles and hair loss.
In order to fully understand the complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors in androgenetic alopecia, further studies are needed. By unraveling the underlying causes, we can develop more targeted treatments and interventions to help women effectively manage this condition.
Diagnosis of Female Pattern Hair Loss
Diagnosing female pattern hair loss involves a thorough evaluation to exclude other potential causes of hair loss, such as thyroid disease or iron deficiency. We consider the appearance and pattern of hair loss, as well as the patient’s medical history, to reach an accurate diagnosis. During the physical examination, we look for signs of increased androgen levels, such as abnormal new hair growth on the face or between the belly button and pubic area.
If necessary, a skin biopsy of the scalp or blood tests may be performed to identify underlying skin disorders or hormonal imbalances that could be contributing to the hair loss. Additionally, dermoscopy or microscopic examination of the hair shaft can help assess its structure. These diagnostic procedures help us rule out other conditions and provide a comprehensive understanding of genetic alopecia in females.
If you are experiencing hair loss that persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, we recommend consulting a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.

Diagnostic Criteria for Female Pattern Hair Loss
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Pattern of hair loss | Thinning of hair primarily at the top of the head and widening of the middle part |
| Medical history | Assessment of previous medical conditions, medications, and family history of hair loss |
| Physical examination | Evaluation of hair loss pattern, signs of increased androgen levels, and presence of other scalp or hair abnormalities |
| Skin biopsy | Biopsy of the scalp to identify underlying skin disorders or inflammation |
| Blood tests | Measurement of hormone levels, such as androgens and thyroid hormones |
| Dermoscopy | Microscopic examination of the hair to assess its structure and determine the stage of hair loss |
Seeking Professional Help
If you’re concerned about hair loss or notice any changes in your hair density or pattern, we encourage you to consult a healthcare provider with experience in hair disorders. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, proper diagnosis, and personalized treatment options to manage female pattern hair loss.
Treatment Options for Genetic Alopecia in Females
While there is no known cure for genetic alopecia in females, there are treatment options available to manage the condition and promote hair growth. One of the most commonly prescribed medications for female pattern hair loss is minoxidil. This FDA-approved medication is applied topically to the scalp and comes in 2% or 5% strength. Minoxidil has been found to stimulate hair growth in about 25-30% of women. However, it’s important to note that the benefits of minoxidil may only be temporary, and hair loss may resume once treatment is stopped.
Other medications may also be prescribed to manage androgenetic alopecia in women. These include:
- Spironolactone: This medication helps block the effects of androgens and may be effective in treating female hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances.
- Cimetidine: Originally used to treat stomach ulcers, cimetidine has also been found to have anti-androgenic effects, making it a potential treatment for genetic alopecia in females.
- Birth control pills: Some forms of oral contraceptives contain hormones that can help regulate androgen levels and prevent hair loss in women.
- Ketoconazole: This antifungal medication has anti-androgenic properties and may be used to manage androgenetic alopecia in women.
In cases where medical treatment is not effective or desired, hair transplant procedures may be considered. These surgical procedures involve the transplantation of hair follicles from areas of the scalp with healthy hair growth to areas affected by hair loss. Hair transplant procedures can provide a more permanent solution for women with genetic alopecia.
For those who prefer non-surgical options, there are alternatives to consider. Hair weaving, hairpieces, and changes in hairstyle can help improve the appearance of hair loss. These non-surgical interventions can be especially helpful for individuals looking for temporary solutions or who want to explore different styles while managing their hair loss.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best treatment options for genetic hair loss in women. A personalized approach can be taken based on the individual’s unique circumstances, severity of hair loss, and desired outcomes.
| Treatment Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Minoxidil | A topical medication that stimulates hair growth. Available in 2% or 5% strength. |
| Spironolactone | A medication that blocks the effects of androgens and helps manage hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances. |
| Cimetidine | An anti-ulcer medication with anti-androgenic properties that may be used to treat genetic alopecia in females. |
| Birth control pills | Oral contraceptives that regulate hormone levels and prevent hair loss in some women. |
| Ketoconazole | An antifungal medication that has anti-androgenic effects and may be used to manage androgenetic alopecia in women. |
| Hair transplant | A surgical procedure that involves the transplantation of hair follicles from areas of the scalp with healthy hair growth to areas affected by hair loss. |
| Hair weaving, hairpieces, and changes in hairstyle | Non-surgical alternatives that can improve the appearance of hair loss and provide temporary solutions. |
Impact and Psychological Effects of Female Hair Loss
Female hair loss can have a significant impact on self-esteem and emotional well-being. Many women experience feelings of distress, embarrassment, and decreased self-confidence as a result of their hair loss. Hair loss can also lead to social discomfort and avoidance of certain activities or situations.
Addressing the psychological effects of female hair loss is crucial. Seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, or consulting mental health professionals can be beneficial in navigating the emotional challenges associated with genetic alopecia.
There are various cosmetic solutions available to improve the appearance of hair loss and boost self-confidence. Wigs, hairpieces, and styling techniques can help women feel more comfortable in their skin. Additionally, counseling or therapy may be recommended to help individuals cope with the emotional impact of hair loss.
“The emotional impact of female hair loss should never be underestimated. It is important to address not only the physical symptoms but also the psychological well-being of those affected.”
– Dr. Rachel Evans, Clinical Psychologist
Psychological Effects of Female Hair Loss:
- Decreased self-esteem and self-confidence
- Feelings of distress, embarrassment, and shame
- Social discomfort and avoidance of certain activities or situations
- Anxiety and depression
- Loss of femininity and identity
Coping Strategies:
While every individual’s experience with female hair loss is unique, here are some strategies that can help cope with the emotional impact:
- Seek emotional support from loved ones, support groups, or mental health professionals.
- Practice self-care activities such as self-acceptance and finding ways to enhance self-esteem.
- Explore cosmetic solutions like wigs, hairpieces, and styling techniques to improve the appearance and boost self-confidence.
- Consider counseling or therapy to develop coping mechanisms and navigate the emotional challenges.
Remember, reaching out for support is a sign of strength, and there are resources available to help individuals cope with the psychological effects of female hair loss.
Managing and Coping with Female Hair Loss
Managing and coping with female hair loss involves a combination of medical treatment, self-care strategies, and emotional support. Following a treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare provider and using medications as directed can help slow down or stop hair loss and promote hair growth.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can contribute to overall hair health. Ensuring adequate nutrition with a focus on essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, biotin, and vitamin D, can support hair growth and thickness.
| Self-Care Strategies for Coping with Female Hair Loss: |
|---|
|
Seeking Emotional Support for Female Hair Loss:
Coping with female hair loss can be emotionally challenging, and seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can provide a safe space to share experiences and gain valuable insights. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can help individuals feel understood and less alone. Professional counseling or therapy may also be recommended for individuals struggling with the emotional impact of female hair loss. Mental health professionals can provide guidance, coping strategies, and tools to manage stress and improve overall well-being.
“Hair loss does not define self-worth.”
Remember, managing and coping with female hair loss is a personal journey, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s essential to find a personalized approach that suits individual needs and preferences. Consulting a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan is crucial. With the right support and strategies in place, it is possible to navigate the challenges of genetic alopecia and embrace one’s natural beauty.
Conclusion
Genetic alopecia, also known as female pattern hair loss, is a common condition that affects millions of women worldwide. While the exact causes are not fully understood, research suggests that a combination of genetic and hormonal factors contribute to its development. Androgens, such as dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a significant role in hair loss, and variations in the AR gene have been associated with this condition.
Diagnosing female pattern hair loss involves ruling out other potential causes and assessing the pattern of hair loss. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. While there is currently no cure for genetic alopecia, several treatment options are available. Medications like minoxidil can help stimulate hair growth, and surgical procedures may be considered for individuals who do not respond well to medical treatment.
Managing the psychological impact of female hair loss is equally important. Seeking emotional support from loved ones, participating in support groups, and practicing self-care strategies can help individuals cope with the challenges associated with genetic alopecia. It is essential to remember that every individual’s experience with hair loss may vary, and finding the right treatment and support system is a personal journey. If you are experiencing hair thinning or hair loss, we encourage you to consult a healthcare professional who can provide guidance and support.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. With the advancements in medical research and the support available, there are options to manage and cope with female pattern hair loss. Seeking help early and taking proactive steps can make a significant difference in enhancing your quality of life and self-confidence. There is hope, and together we can navigate through the challenges of genetic alopecia.
FAQ
What is genetic alopecia in females?
Genetic alopecia in females, also known as female pattern hair loss, is a common form of hair loss characterized by thinning of the hair at the top of the head and widening of the middle part.
What causes androgenetic alopecia in females?
Androgenetic alopecia in females is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, including changes in hormone levels, aging, and a family history of male or female pattern baldness.
How is female pattern hair loss diagnosed?
Diagnosis of female pattern hair loss involves ruling out other potential causes of hair loss and evaluating the pattern of hair loss. Physical examination, medical history, and sometimes blood tests or scalp biopsies may be conducted.
What are the treatment options for genetic alopecia in females?
Treatment options for genetic alopecia in females include the use of medications such as minoxidil and spironolactone. In some cases, hair transplant procedures may be considered. Non-surgical options like hairpieces or changes in hairstyle can also be helpful.
What are the psychological effects of female hair loss?
Female hair loss can have a significant impact on self-esteem and emotional well-being, leading to distress, embarrassment, and decreased self-confidence. It can also result in social discomfort and avoidance of certain activities or situations.
How can females manage and cope with hair loss?
Managing and coping with female hair loss involves following a treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare provider, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing self-care strategies, and seeking emotional support from loved ones or professionals.
Is there a cure for genetic alopecia in females?
Currently, there is no known cure for genetic alopecia in females. However, there are treatment options available to manage the condition and promote hair growth.

