Ever wondered why your hair seems thinner or your scalp more visible? Hair loss, or alopecia, is common among both men and women. It can be caused by many things, like genetics, medical issues, and lifestyle choices.
In this article, we’ll explore the complex world of scalp hair thinning. We’ll look at the many factors that lead to this issue. Whether it’s male-pattern baldness, female-pattern hair loss, or other types of alopecia, knowing the causes is key to finding a solution.
Key Takeaways
- Scalp hair thinning can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, age, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices.
- Androgenetic alopecia, the most common type of hair loss, affects both men and women and is often hereditary.
- Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders and nutritional deficiencies, can contribute to hair loss.
- Cancer treatments and some medications can also lead to temporary or permanent scalp hair thinning.
- Proper hair care, stress management, and addressing underlying health issues can help maintain a healthy head of hair.
Understanding Scalp Hair Thinning
Scalp hair thinning, also known as alopecia, is a common issue. It leads to hair loss on the scalp. This can show up as hair thinning on top, circular bald spots, or hair falling out suddenly.
There are many reasons for scalp hair thinning. These include genetics, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices.
What is Scalp Hair Thinning?
An adult’s head has 100,000 to 150,000 hairs. Losing up to 100 hairs a day is normal. But, scalp hair thinning means losing more hair than usual.
About 90% of scalp hair is growing at any time. The other 10% is resting before it falls out.
Common Causes of Scalp Hair Thinning
The main reasons for scalp hair thinning are:
- Family history (heredity): Some people are more likely to lose hair because of their genes. Men can start losing hair in their teens or early 20s. Women often notice thinning in their 40s or later.
- Hormonal changes: Hormone shifts, like during pregnancy or menopause, can cause hair thinning.
- Medical conditions: Issues like thyroid problems, alopecia areata, and not getting enough nutrients can lead to hair loss.
- Medications and treatments: Some drugs, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy can cause hair to fall out.
- Stress and lifestyle factors: Too much stress, tight hairstyles, and overusing hair treatments can also cause thinning hair.
Knowing why you’re losing hair is the first step to finding a solution.
Hereditary and Age-Related Hair Loss
Scalp hair thinning often comes from a hereditary condition called androgenic alopecia, or male and female pattern baldness. Men usually see a receding hairline and bald spots on top. Women notice thinning hair, especially along the part line and crown.
Androgenic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)
In the U.S., androgenetic alopecia affects 50 million men and 30 million women. Over 50 percent of men over 50 experience hair loss. Women often see thinning after menopause.
Research links androgen levels to hair loss with conditions like heart disease and prostate cancer in men. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome also face hair loss.
Age and Natural Hair Loss
As we age, natural hair loss becomes common. Hair growth slows, and follicles stop producing new hair. Hair also loses color, turning gray or white.
A woman’s hairline may recede with age. Androgenetic alopecia can start in the teens, with risk increasing with age.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Hair growth rate | On average, hair grows half an inch per month and six inches per year. |
| Hair loss with aging | Nearly everyone experiences some form of hair loss with aging. |
| Hair changes during menopause | Women and individuals assigned female at birth may experience significant hair changes during menopause in their 40s. |
| Hair thinning with age | Hair fibers become thinner over time, leading to hair loss that does not regenerate. |
| Hair color changes with age | Pigment cells in hair decrease with age, leading to changes in hair color. |

To keep hair healthy with age, wash the scalp twice a week. Eat a diet rich in protein and avoid too much heat styling. Some medications and endocrine disorders can affect hair growth. If you notice significant hair loss, talk to a healthcare provider.
Medical Conditions Causing Scalp Hair Thinning
Many medical conditions can lead to thinning hair or hair loss on the scalp. It’s key to know the causes to manage and treat this issue well.
Alopecia Areata (Autoimmune Disorder)
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder. It happens when the body attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss on the scalp and elsewhere. It affects about 2% of people, leading to sudden, round bald spots.
Thyroid Disorders
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can make hair thin or fall out in clumps. Thyroid problems disrupt hair growth, causing noticeable loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Lack of biotin, iron, protein, and zinc can also cause hair thinning. These nutrients are vital for healthy hair growth.
If you notice your hair thinning without reason, see a doctor. They can find the cause and help you get better.
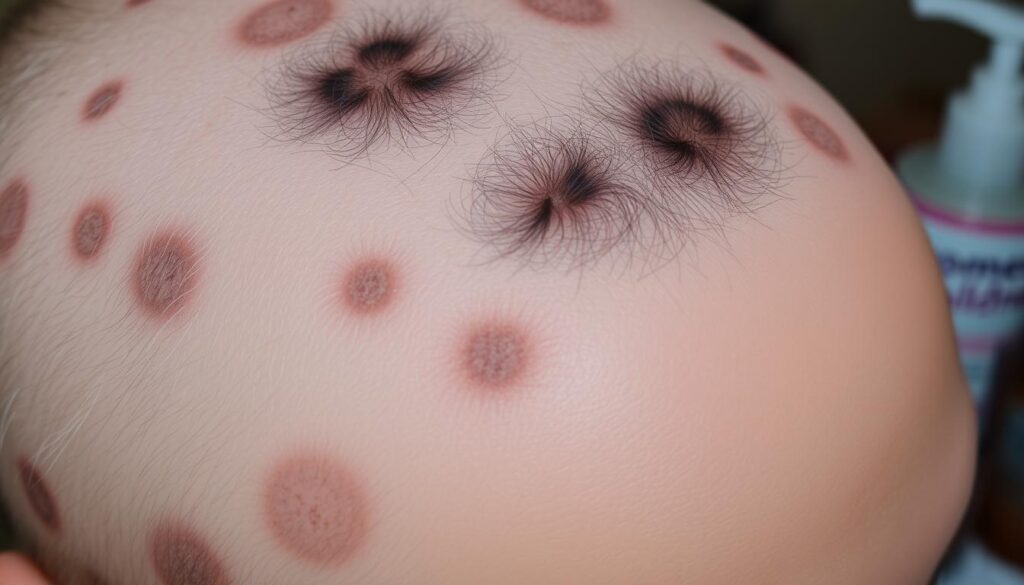
Scalp Hair Thinning Caused by Medications and Treatments
Some medicines and treatments can harm our scalp hair, causing it to thin or fall out. It’s important to know how these factors affect hair loss. This knowledge helps us manage and treat the problem better.
Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can lead to severe hair loss, especially on the head or neck. This happens because these treatments harm the hair follicle cells. They disrupt the normal hair growth cycle.
Anagen effluvium is a type of hair loss linked to chemotherapy. It can cause people to lose most or all of their hair, including eyebrows and eyelashes. Hair loss from chemotherapy usually starts within 2 weeks and gets worse after 1 to 2 months.
Certain Prescription Drugs
Some prescription drugs, like those for cancer, arthritis, and heart problems, can cause hair loss. Telogen effluvium is the most common drug-induced hair loss. It can start 2 to 4 months after starting the drug, leading to more hair shedding than usual.
Drugs that might cause hair loss include antifungal drugs, seizure medications, and beta-blockers. If you think a drug is causing your hair to thin, talk to your doctor right away.
Hair loss from medicines is usually temporary. Hair growth usually returns when the drug stops. But in rare cases, it can be permanent. Getting professional advice and looking into other treatment options can help prevent permanent hair loss.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Thinning Hair
Genetics and medical conditions can cause hair thinning. But, our daily choices also play a big part. Tight hairstyles, stress, and hormonal changes can harm our hair. Knowing these factors helps keep our hair healthy and full.
Hairstyles and Hair Care Practices
Hairstyles like ponytails and braids can cause hair loss called traction alopecia. Harsh treatments like coloring and perming also damage hair. Choose gentler styles and treatments to protect your hair.
Stress and Hormonal Imbalances
Stress and hormonal changes, like during pregnancy or menopause, can lead to hair loss. Managing stress and keeping hormones balanced can help prevent this.
Knowing how hairstyles, hair care, stress, and hormones affect hair thinning is key. Use gentle styles, reduce stress, and get medical help for hormonal issues. These steps can help keep your hair thick and healthy.
“Up to 40% of women will experience noticeable hair loss by age 50, and women can lose between 50 and 100 strands of hair each day, which is considered normal.”
Treating and Managing Scalp Hair Thinning
If you’re dealing with scalp hair thinning, there are many ways to help. You can try over-the-counter solutions, prescription meds, or even surgery in some cases.
Over-the-Counter and Prescription Treatments
Minoxidil, or Rogaine, is a common over-the-counter treatment. It helps grow hair and stop more loss. But, it takes about 6 months to see results. Adding essential oils like peppermint or rosemary to your hair care can also boost growth. Anti-thinning shampoos with saw palmetto or biotin are also good choices.
For serious hair thinning, your doctor might suggest spironolactone or finasteride. Spironolactone works for female pattern baldness. Finasteride is often used for male hair loss. But, finasteride might not work as well for men over 60.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
There are also home remedies and lifestyle changes to help with hair thinning. Scalp massage can boost blood flow and help hair grow. Taking multivitamins, folic acid, and biotin can also support hair health. Getting enough omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is also good for your hair.
Finding the right treatment for scalp hair thinning depends on the cause and your needs. It’s key to work with a healthcare pro to create a plan that’s right for you.
Conclusion
Scalp hair thinning is a complex issue with many causes. These include hereditary factors, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. While some hair loss can’t be stopped, knowing the causes and trying treatments can help keep our hair full and healthy.
By tackling the causes of thinning hair, like genetics, hormones, diet, or medication side effects, we can fight it. Using both over-the-counter and prescription treatments, along with lifestyle changes, can help. This approach can lead to healthier hair growth.
The best way to deal with thinning hair is to understand it well. We should be open to trying different treatments and care for our hair healthfully. By doing so, we can feel confident and look youthful again.
Source Links
- Hair loss – Symptoms and causes
- Hair loss: Who gets and causes
- Types of Hair Loss
- The Basics of Hair Loss
- 12 Ways to Stop Hair Thinning
- Androgenetic alopecia: MedlinePlus Genetics
- Your Guide To Aging, Thinning Hair: 5 Simple Tips
- How to Maintain Hair Growth After 50
- Hidden Causes of Hair Loss
- Thinning hair: Causes, types, treatment, and remedies
- Drug-Induced Hair Loss
- Medications That Cause Hair Loss: List, What You Can Do, and More
- How to reverse hair loss from medication
- What causes female hair loss?
- Is Thin Hair Stressing You Out? Here’s What to Know and Do About It
- Hair loss – Diagnosis and treatment
- Hair loss: Diagnosis and treatment
- Male Androgenetic Alopecia – Endotext
- Hair Loss: Common Causes and Treatment