We’ve all felt it – when we run our fingers through our hair and find a bunch of strands. Hair shedding is normal, but too much can worry us. But how much is too much, and what does it mean for our health? We’ll dive into the science of scalp hair shedding and find out the causes and solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Scalp hair shedding is a normal part of the hair growth cycle, but excessive shedding can be a sign of an underlying health condition.
- Factors like stress, hormonal changes, and certain medical treatments can contribute to increased hair loss.
- Identifying the root cause of excessive shedding is crucial for finding the right treatment approach.
- Adopting healthy hair care practices and addressing any underlying issues can help manage and reduce scalp hair shedding.
- Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.
What is Scalp Hair Shedding?
The scalp has about 100,000 hairs. These hairs go through growing, resting, falling out, and regrowing. Losing 50 to 100 hairs a day is normal.
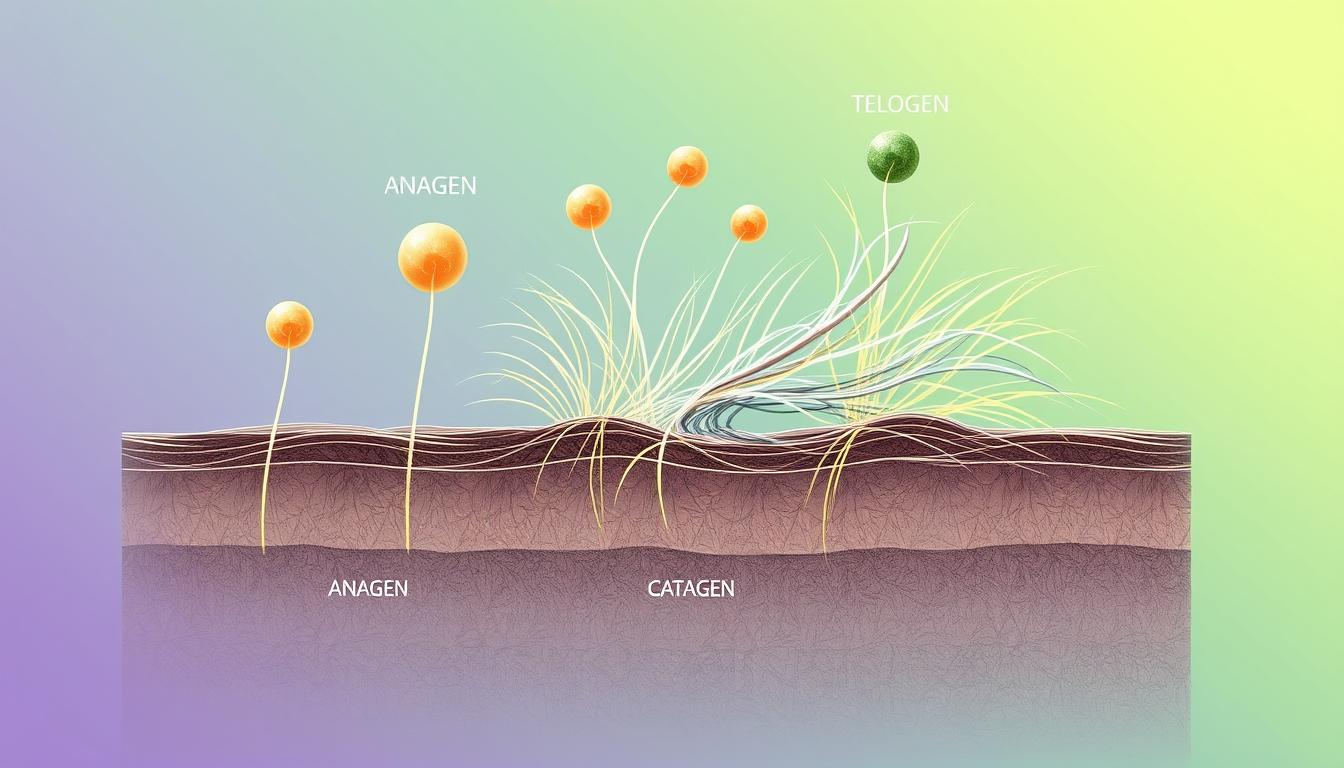
Hair Growth Cycle and Normal Hair Loss
The hair growth cycle has three main phases:
- Anagen (growth) phase: This phase accounts for 80-90% of hair follicles and lasts 2-6 years.
- Catagen (transition) phase: This phase accounts for 5% of hair follicles and lasts about 2-3 weeks.
- Telogen (resting) phase: This phase accounts for 10-15% of hair follicles and lasts about 3 months before the hair is shed.
During the exogen phase, 50-100 hairs are shed per day. This is a normal part of the hair growth cycle.
Signs and Symptoms of Excessive Shedding
If the hair growth cycle is disrupted, hair may fall out faster. Signs of excessive hair shedding include:
- Gradual thinning on top of the head
- Circular or patchy bald spots
- Sudden loosening of hair
- Full-body hair loss
Sudden or patchy hair loss means you might have a medical issue that needs attention.
“Typically, 50–100 hairs are shed each day, depending on combing and washing routines.”
| Hair Growth Phase | Duration | Percentage of Hair Follicles |
|---|---|---|
| Anagen (Growth) | 2-6 years | 80-90% |
| Catagen (Transition) | 2-3 weeks | 5% |
| Telogen (Resting) | 3 months | 10-15% |
Causes of Scalp Hair Shedding
Hair loss can come from many sources. These include genetics, hormonal shifts, and medical issues. Knowing why hair falls out is key to fixing the problem.
Hormonal Imbalances and Medical Conditions
Hormonal changes, like those during pregnancy or menopause, can cause hair loss. Thyroid problems, such as too little or too much thyroid hormone, also lead to hair shedding. Besides, conditions like alopecia areata and scalp infections can cause hair to fall out.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause
- Thyroid disorders (hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism)
- Alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition
- Scalp infections
Medical issues like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also cause hair loss. Some medicines, especially those for cancer, can make hair fall out too.

Seeing a doctor is crucial. They can find out why hair is falling out and help fix it.
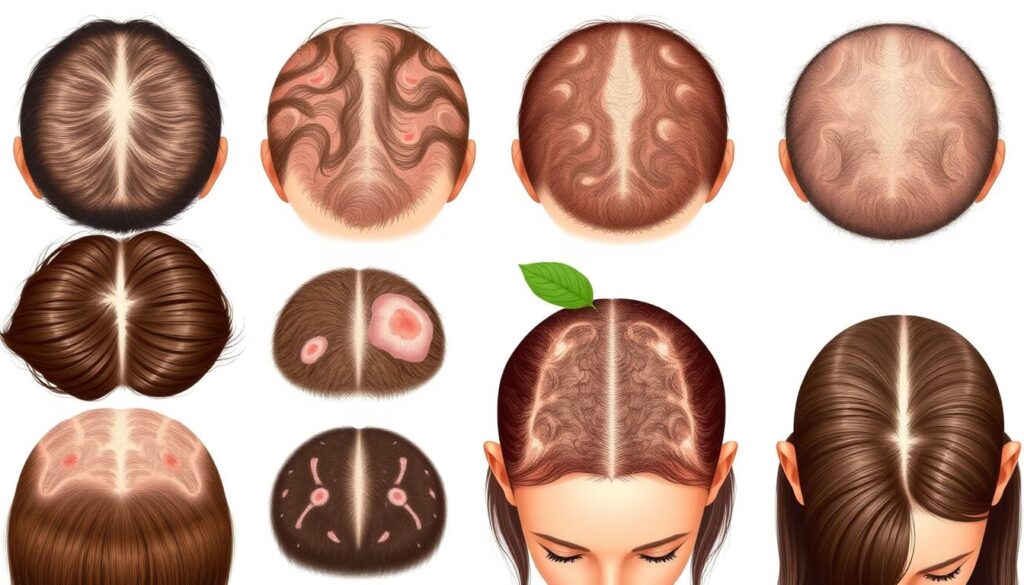
Types of Hair Loss
Hair loss is a common concern that can take various forms. The most prevalent types of hair loss include:
- Androgenetic alopecia – Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this is the most frequent type of hair loss, affecting up to 50% of individuals by the age of 50.
- Telogen effluvium – Excessive shedding triggered by physical or emotional stress, hormonal changes, or medical conditions.
- Anagen effluvium – Rapid hair loss caused by medical treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Alopecia areata – An autoimmune condition that results in patchy hair loss, which can sometimes lead to total hair loss.
Other less common types of hair loss include tinea capitis (scalp ringworm) and various forms of cicatricial alopecia (scarring hair loss). The cause, severity, and prognosis of hair loss can vary significantly. This highlights the importance of seeking professional medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.

“Hair loss can be a distressing and complex issue, but understanding the different types and their causes is the first step towards effective management.”
Scalp Hair Shedding and Its Impact
Excessive scalp hair shedding can greatly affect how someone looks and feels about themselves. It can cause anxiety, depression, and make people withdraw from social activities. Getting medical help and support is key to dealing with these feelings.
Research shows that male hair loss affects 30-50% of men by age 50. Most of this is due to genetics. The FDA has approved treatments like topical minoxidil and oral finasteride. Hair transplantation can also be very effective, with a success rate over 90%.
Hair loss can really affect a person’s mental health. Men who lose their hair may feel sad, anxious, and struggle to connect with others. They might also face a higher risk of heart disease, making early treatment even more important.
“Negative self-perception of balding patients has a significant psychological impact.”
Women can also experience hair loss, often in their 40s or later. Conditions like alopecia areata and telogen effluvium can cause hair shedding. These issues can also affect a person’s mental health.
Understanding the impact of hair shedding and getting medical care can help. It can improve how someone feels about themselves and their overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding why we lose hair is key to managing it better. Some hair loss is hereditary, but we can still take steps to help. We can prevent or manage some types of hair shedding.
Being gentle with our hair and protecting it from UV rays helps a lot. Also, treating any health issues or nutritional problems is crucial. Working with doctors to create a treatment plan can make a big difference in keeping our hair healthy.
It’s also important to deal with the emotional side of hair loss. Losing hair can affect how we feel and how we interact with others. Counseling and therapy can help those dealing with hair loss. They offer support and tools to face this challenge.
Source Links
- Types of Hair Loss
- Telogen Effluvium: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Regrowth
- Normal Shedding vs. Hair Loss Explained by a Dermatologist – Dove
- Hair shedding
- Wimpole Hair Transplant Clinic
- How Much Hair Loss Is Normal: Everyone Sheds
- Hair loss – Symptoms and causes
- Hair loss: Who gets and causes
- Hair loss, balding, hair shedding, alopecia
- Everything You Need to Know About Hair Loss
- Thinning hair: Causes, types, treatment, and remedies
- Male Androgenetic Alopecia – Endotext
- The Basics of Hair Loss
- Telogen effluvium: Symptoms, treatment, and recovery
- Hair Loss: Common Causes and Treatment
- Psychology of Hair Loss Patients and Importance of Counseling