Did you know that hair loss affects approximately 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States alone? Hair loss, also known as alopecia, is a common condition that can have a significant impact on individual self-esteem and overall well-being. While it may seem alarming, understanding the reasons behind hair loss is the first step towards effective management and treatment. In this article, we will explore the various causes of hair loss and provide valuable insights for preventing and addressing this concern.
Key Takeaways:
- Hair loss affects millions of men and women in the United States.
- Understanding the causes of hair loss is crucial for effective management.
- This article will provide insights into preventing and addressing hair loss.
Hereditary Hair Loss: Male Pattern Baldness and Female Pattern Hair Loss
Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss worldwide. In men, it is referred to as male pattern baldness, while in women, it is called female pattern hair loss. This type of hair loss occurs due to inherited genes that cause the hair follicles to shrink and eventually stop producing new hair.
Symptoms of hereditary hair loss include gradual thinning of hair, receding hairline in men, and overall hair thinning in women. While men tend to experience a distinct pattern of baldness, with hair thinning starting at the crown and temple areas, women usually have diffuse hair loss throughout the scalp. Both sexes may see a reduction in hair volume and density.
This image illustrates the typical patterns of hair loss in men and women:
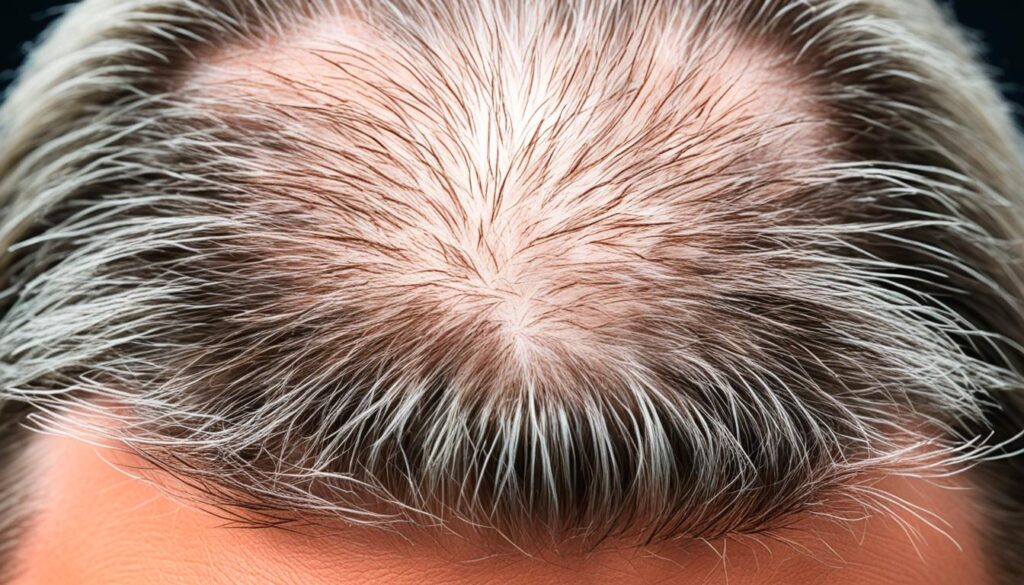
“Hereditary hair loss affects millions of men and women worldwide. Understanding the patterns and symptoms associated with male pattern baldness and female pattern hair loss is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.”
Other Factors Contributing to Hair Loss
In addition to hereditary factors, there are several other factors that can contribute to hair loss. Understanding these factors can help in identifying the root cause of hair loss and implementing appropriate measures for management and prevention.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances, such as those caused by conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can play a significant role in hair loss. PCOS is a common hormonal disorder that affects women and can lead to excessive hair growth in certain areas and thinning of hair on the scalp. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause can also contribute to hair loss in women.
Poor Hair Care Practices
The way we care for our hair can have a direct impact on its health and growth. Excessive hairstyling, including tight hairstyles and frequent use of heat styling tools, can cause physical stress on the hair follicles and lead to hair loss. Pulling the hair tightly can result in a condition called traction alopecia, where constant tension causes the hair to weaken and fall out. Additionally, using harsh chemicals, such as certain hair dyes and relaxers, can damage the hair shaft and contribute to hair loss.
Scalp Infections
Scalp infections, such as fungal infections like ringworm, can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle and result in hair loss. These infections can cause inflammation and damage to the hair follicles, leading to weakened or dormant hair growth. It is important to maintain good scalp hygiene and seek medical treatment if you suspect a scalp infection.
Medication
Certain medications can have side effects that include hair loss. These medications may interfere with the normal hair growth cycle and cause temporary or permanent hair loss. Some examples include medications used for cancer treatment, antidepressants, blood thinners, and certain blood pressure medications. If you are experiencing hair loss while taking any medications, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if the medication could be a contributing factor.
Medical Conditions and Treatments Leading to Hair Loss
Certain medical conditions and treatments can contribute to hair loss. It is important to understand how these factors can affect hair health and seek appropriate management and treatment options. In this section, we will explore three significant factors that can lead to hair loss: alopecia areata, cancer treatment, and thyroid disease.
Alopecia Areata

Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss. This condition affects both men and women of all ages. The exact cause of alopecia areata is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The hair loss can occur rapidly and may result in total scalp hair loss (alopecia totalis) or complete hair loss on the scalp and body (alopecia universalis).
Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy, often result in temporary hair loss. These treatments target rapidly dividing cancer cells, and unfortunately, hair follicles also fall into this category. As a result, hair loss is a common side effect. The extent and duration of hair loss may vary depending on the specific treatment regimen and individual factors. It is important to note that hair growth usually resumes once the treatment is completed, although the texture and color of the new hair may differ temporarily.
Thyroid Disease
Thyroid diseases, such as hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid), can have a direct impact on hair health. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and hormone production. Imbalances in thyroid hormone levels can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to hair thinning and loss. Individuals with thyroid disease may experience changes in hair texture, dryness, and increased hair shedding. Appropriate management of thyroid disease can help improve hair health and minimize further hair loss.
In summary, alopecia areata, cancer treatment, and thyroid disease are medical conditions and treatments that can contribute to hair loss. If you or someone you know is experiencing hair loss due to these factors, it is recommended to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Lifestyle Factors and Hair Loss
Lifestyle factors can have a significant impact on hair loss. From hormonal changes during childbirth to the effects of stress and poor nutrition, these factors can contribute to the loss of hair. Understanding how these lifestyle factors affect hair health is essential for effective management and prevention of hair loss.
Childbirth and Hair Loss
For women, hormonal changes during and after childbirth can result in temporary hair loss. The fluctuating levels of hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle. This disruption can lead to increased hair shedding and thinning. However, it’s important to note that the hair typically regrows naturally within a few months after childbirth.
Stress and Hair Loss
Stress, whether physical or emotional, can also contribute to hair loss. When the body is under stress, it directs its energy towards essential functions, diverting resources away from non-essential processes like hair growth. This can result in increased hair shedding and slower hair regrowth. Chronic stress can have a prolonged impact on hair health, leading to more severe hair loss conditions like telogen effluvium or alopecia areata.
Nutrition and Hair Loss
Poor nutrition can negatively affect hair growth and lead to hair loss. Nutritional deficiencies, especially in essential vitamins and minerals like biotin, iron, protein, and zinc, can impair the hair follicles’ ability to produce healthy hair strands. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods is crucial for maintaining optimal hair health.
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Hair Loss |
|---|---|
| Childbirth | Temporary hair loss due to hormonal changes |
| Stress | Can contribute to increased hair shedding and slow regrowth |
| Nutrition | Poor nutrition can impair hair growth and lead to hair loss |
Conclusion
Understanding hair loss is crucial for managing and preventing its occurrence. Whether it is caused by hereditary factors, hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, lifestyle choices, or treatments, identifying the root cause is the first step towards effective management.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the individual’s specific situation.
In addition, taking care of overall health plays a vital role in promoting hair health and preventing hair loss. Maintaining a balanced diet that includes essential nutrients like biotin, iron, protein, and zinc can support healthy hair growth. Managing stress levels and practicing healthy hair care routines, such as avoiding excessive hairstyling and using gentle products, can also contribute to maintaining the integrity of the hair.
In conclusion, by understanding the underlying causes of hair loss and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals can take control of their hair health. With the guidance of healthcare professionals and by making conscious lifestyle choices, it is possible to manage and prevent further hair loss.
FAQ
Why does hair loss happen?
Hair loss can occur due to various reasons, including hereditary factors, hormonal changes, medical conditions, aging, and certain lifestyle and environmental factors.
What is hereditary hair loss?
Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss worldwide. In men, it is referred to as male pattern baldness, while in women, it is called female pattern hair loss.
What are some other factors that contribute to hair loss?
Other factors that can contribute to hair loss include hormonal imbalances, poor hair care practices, scalp infections, certain medications, and certain hairstyles that pull on the scalp.
Can medical conditions and treatments lead to hair loss?
Yes, certain medical conditions such as alopecia areata and thyroid diseases, as well as certain treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can cause hair loss.
Can lifestyle factors affect hair loss?
Yes, lifestyle factors such as hormonal changes during and after childbirth, stress, and poor nutrition can contribute to hair loss.

