Have you ever wondered why some women experience hair loss while others maintain a full and healthy head of hair? Is it simply a matter of genetics, or are there other factors at play? In this article, we will delve into the different types of hair loss that affect women and explore their unique characteristics and causes. By understanding these types, we can gain insight into effective treatment options and strategies for managing female hair loss.
Key Takeaways:
- There are several types of hair loss that affect women, including androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, anagen effluvium, alopecia areata, tinea capitis, cicatricial alopecia, and hair shaft abnormalities.
- Each type of hair loss has its own unique characteristics and causes, ranging from genetics and hormonal imbalances to autoimmune conditions and fungal infections.
- Proper diagnosis by a dermatologist or healthcare professional is crucial to determine the underlying cause of hair loss and develop an effective treatment plan.
- Early intervention and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for women experiencing hair loss, so don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you’re concerned about your hair.
- Remember, you’re not alone in your hair loss journey, and there are resources and support available to help you navigate this often challenging experience.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as female pattern hair loss, is the most common type of hair loss in both men and women. It is hereditary and can be managed with medication or surgery. In women, androgenetic alopecia usually presents as overall thinning of the hair, with the hairline typically not receding.
This type of hair loss can be caused by hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), as well as genetics. Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle and lead to hair thinning and loss. Additionally, genetic factors play a significant role, as individuals with a family history of androgenetic alopecia are more likely to experience this condition.
Topical minoxidil (Rogaine) and oral medications like spironolactone or finasteride are common treatment options for androgenetic alopecia in women. Minoxidil, a topical solution, helps to stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss. Oral medications like spironolactone and finasteride work by addressing hormonal imbalances and promoting hair regrowth.

Comparison of Treatment Options for Androgenetic Alopecia
| Treatment | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Minoxidil (Rogaine) | A topical solution applied to the scalp to stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss. | Apply twice daily to affected areas. |
| Spironolactone | An oral medication that helps address hormonal imbalances, which can contribute to hair loss. | Take once or twice daily as prescribed by a healthcare professional. |
| Finasteride | An oral medication that targets hormonal imbalances and promotes hair regrowth. | Take once daily as prescribed by a healthcare professional. |
It’s important to note that treatment effectiveness may vary depending on individual factors, and it’s best to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional for personalized recommendations. Early intervention and proper treatment can significantly improve outcomes for women experiencing hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a common type of hair loss that affects many women. It is characterized by excessive shedding of hair all over the scalp, resulting in noticeable thinning.
This condition occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle, known as the telogen phase, prematurely. As a result, the next growth phase, called the anagen phase, is delayed. This disrupts the normal hair growth process and leads to increased hair loss.
Telogen effluvium can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders
- Nutritional deficiencies, particularly of iron, zinc, or biotin
- Sudden weight loss or crash dieting
- Physical or emotional stress, such as a major illness, surgery, or a traumatic event
- Certain medications or medical treatments, like chemotherapy
It is important to note that telogen effluvium is often temporary and resolves on its own once the underlying cause is addressed. However, it can take several months for the hair to fully recover and for normal hair growth to resume.
Treatment for telogen effluvium focuses on addressing the underlying cause and promoting hair regrowth. This may include:
- Managing stress through techniques like relaxation exercises or therapy
- Addressing nutritional deficiencies through a balanced diet or supplements
- Using medications, such as minoxidil, to stimulate hair growth
It is recommended to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of telogen effluvium and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
“Telogen effluvium is a temporary condition that can be distressing for women. However, with proper management and treatment, it is possible to restore healthy hair growth and regain confidence.”
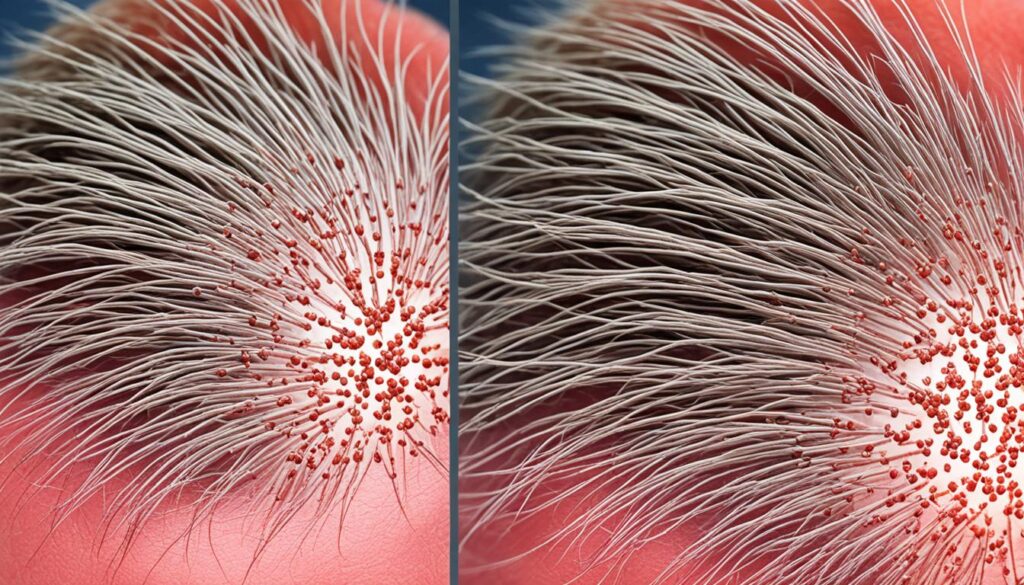
By understanding the causes and treatment options for telogen effluvium, women can take proactive steps towards managing their hair loss and promoting regrowth.
Anagen Effluvium
Anagen effluvium is a type of hair loss commonly experienced by women undergoing medical treatments such as chemotherapy. These treatments target rapidly dividing cells in the body, including the hair follicles, which can result in significant hair loss. Hair loss caused by anagen effluvium is characterized by rapid shedding and the fracture of hair shafts.
Once the medical treatment is completed, hair usually starts to grow back on its own. However, the regrowth process may take time, and the texture or color of the hair may differ initially. In some cases, additional treatments or medications may be necessary to stimulate hair regrowth and improve the overall appearance of the hair.
While anagen effluvium can be a challenging experience, understanding the causes and available treatments can help women effectively manage their hair loss and regain confidence in their appearance.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that affects women and causes hair loss. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to patches of hair loss on the scalp. Although it commonly affects the scalp, it can also occur on other areas of the body, including the eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
The exact cause of alopecia areata is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes are associated with an increased risk of developing this condition, and it often occurs in individuals with a family history of autoimmune diseases. Environmental triggers, such as stress or viral infections, may also contribute to the development of alopecia areata.
There is currently no known cure for alopecia areata, but there are treatment options available to help manage the condition and promote hair regrowth. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the hair loss and individual preferences. Some common treatment options include:
- Topical medications: These are applied directly to the affected areas and may include corticosteroids or minoxidil.
- Intralesional corticosteroid injections: These injections are administered into the bald patches to help stimulate hair regrowth.
- Systemic medications: Oral medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, may be prescribed for more severe cases of alopecia areata.
- Support groups: Joining support groups or seeking counseling can be beneficial for individuals dealing with the emotional impact of hair loss.
It is important for women experiencing hair loss due to alopecia areata to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and offer support throughout the process.
“Alopecia areata can have a significant impact on a person’s self-esteem and emotional well-being. Seeking support from others who understand can be incredibly helpful in coping with the challenges of hair loss.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Dermatologist
Tinea Capitis
Tinea capitis, also known as scalp ringworm, is a fungal infection that commonly affects children and can cause hair loss. The infection presents as patchy hair loss on the scalp, accompanied by redness, scaling, and itching.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing tinea capitis and preventing further hair loss. Antifungal medications, such as oral antifungal agents or medicated shampoos, are typically prescribed to treat the infection and promote hair regrowth. Topical antifungal creams are generally not effective in treating tinea capitis because the infection resides deep within the hair follicles.
It’s important to note that tinea capitis is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated objects, such as combs, brushes, and hats. Proper hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and avoiding sharing of personal items, can help prevent the spread of the infection.
If your child shows symptoms of tinea capitis, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional, preferably a dermatologist, for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early intervention and effective management of tinea capitis can minimize hair loss and prevent complications.
“Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing tinea capitis and preventing further hair loss.”
The table below outlines key information about tinea capitis:
| Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Tinea capitis is caused by fungal infection, primarily by dermatophytes belonging to the Trichophyton and Microsporum genera. | – Patchy hair loss on the scalp – Redness, scaling, and itching – Presence of black dots (broken hair shafts) or gray patches on the scalp – Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck |
– Oral antifungal medications (prescription-only) – Medicated shampoos containing antifungal agents – Good scalp hygiene practices – Avoidance of sharing personal items |
Early detection, proper treatment, and maintaining good hygiene practices are key to managing and preventing the spread of tinea capitis. By addressing the underlying fungal infection, hair regrowth can be promoted, and further hair loss can be minimized. Seek professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
Cicatricial Alopecia
Cicatricial alopecia, also known as scarring alopecia, is a rare type of hair loss characterized by the destruction of hair follicles and the formation of scar tissue. This condition can cause gradual or sudden hair loss, along with symptoms like severe itching, swelling, and lesions on the scalp.
The underlying causes of cicatricial alopecia are not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to immune system disorders and inflammation.
| Treatment Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Topical or oral medications | These medications can help manage inflammation and promote hair regrowth in some cases. |
| Laser therapy | Using laser technology to stimulate hair follicles and encourage regrowth. |
| Hair transplantation | Surgical procedure that involves transferring healthy hair follicles to areas affected by cicatricial alopecia. |
It is important to note that the treatment options for cicatricial alopecia depend on the specific type and severity of the condition. Consultation with a dermatologist or healthcare professional is recommended to determine the most suitable approach for individual cases.
Conclusion
Experiencing hair loss can be a distressing situation for women. However, understanding the various types and causes of hair loss is crucial for effective management and treatment. We have explored the different types of hair loss in women, including androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, anagen effluvium, alopecia areata, tinea capitis, cicatricial alopecia, and hair shaft abnormalities.
Each type of hair loss has its own unique characteristics and treatment options. It is important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of hair loss and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Early intervention and proper treatment can make a significant difference in the outcomes for women experiencing hair loss.
Whether it’s female pattern hair loss, temporary hair shedding, or hair loss caused by medical conditions or infections, seeking professional help can provide guidance and support. Our main goal is to empower women to take control of their hair loss journey and regain their confidence. Remember, you are not alone in this, and there are effective treatments available to help you manage and overcome hair loss.
FAQ
What are the types of hair loss that affect women?
The types of hair loss that affect women include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, anagen effluvium, alopecia areata, tinea capitis, cicatricial alopecia, and hair shaft abnormalities.
What is androgenetic alopecia?
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern hair loss or female pattern hair loss, is the most common type of hair loss in both men and women. It is hereditary and can be managed with medication or surgery.
What causes androgenetic alopecia in women?
Androgenetic alopecia in women can be caused by hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), as well as genetics.
What are the treatment options for androgenetic alopecia in women?
Treatment options for androgenetic alopecia in women include topical minoxidil (Rogaine) and oral medications like spironolactone or finasteride.
What is telogen effluvium?
Telogen effluvium is a type of hair loss characterized by the shedding of hair all over the scalp. It occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle, but the next growth phase is delayed.
What can trigger telogen effluvium in women?
Telogen effluvium in women can be triggered by hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, childbirth, surgery, and certain medications.
Is telogen effluvium permanent?
In most cases, telogen effluvium is temporary and resolves on its own after the underlying cause is addressed.
What are the treatment options for telogen effluvium?
Treatment options for telogen effluvium include managing stress, addressing nutritional deficiencies, and using medication if necessary.
What is anagen effluvium?
Anagen effluvium is a type of hair loss that occurs as a result of medical treatments, such as chemotherapy. It is characterized by rapid hair loss and the fracture of hair shafts.
Will hair grow back after anagen effluvium?
After medical treatment ends, hair usually grows back on its own. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help stimulate hair regrowth.
What is alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It typically presents as patchy hair loss on the scalp, but can also affect other areas of the body.
What are the treatment options for alopecia areata?
Treatment options for alopecia areata include medications that can help promote hair regrowth, as well as support groups for individuals with this condition.
What is tinea capitis?
Tinea capitis, also known as scalp ringworm, is a fungal infection that can cause hair loss in children. It presents as patchy hair loss on the scalp, often accompanied by redness, scaling, and itching.
How is tinea capitis treated?
Tinea capitis is typically treated with antifungal medications to eliminate the infection and promote hair regrowth.
What is cicatricial alopecia?
Cicatricial alopecia, also known as scarring alopecia, is a rare type of hair loss characterized by the destruction of hair follicles and the formation of scar tissue.
What causes cicatricial alopecia?
The underlying causes of cicatricial alopecia are not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to immune system disorders and inflammation.
What are the treatment options for cicatricial alopecia?
Treatment options for cicatricial alopecia depend on the specific type and may include topical or oral medications, as well as laser therapy or hair transplantation.

